Wouldn’t You Go to Prison to Help End This War?
Edward Snowden drops his 2nd NFT (after selling the first one for $5.1m). Here is why it's important.
First things first: PleasrDAO, a DAO collective of high profile crypto people, will drop a 1:1 Ethereum NFT entitled:
“Wouldn’t You Go to Prison to Help End This War?”
tomorrow 12.1., 3pm ET. The auction will be live and you can access it here.
The NFT was developed together with Edward Snowden and Daniel Ellsberg and pays tribute to Ellsberg’s 1971 release of the Pentagon Papers.
Why “War”? Let’s dig in.
Snowden sold his first NFT named “Stay Free” in April 2021 for $5.1m to PleasrDAO, to fund the Freedom of the Press Foundation.
“Stay Free” combines the entirety of a landmark court decision ruling the National Security Agency's mass surveillance violated the law, with the iconic portrait of the whistleblower, signed by Edward Snowden.
Why is this symbolic?
Privacy and freedom underpin the core philosophies of Web3, crypto and ultimately Bitcoin.
The origins of Web3
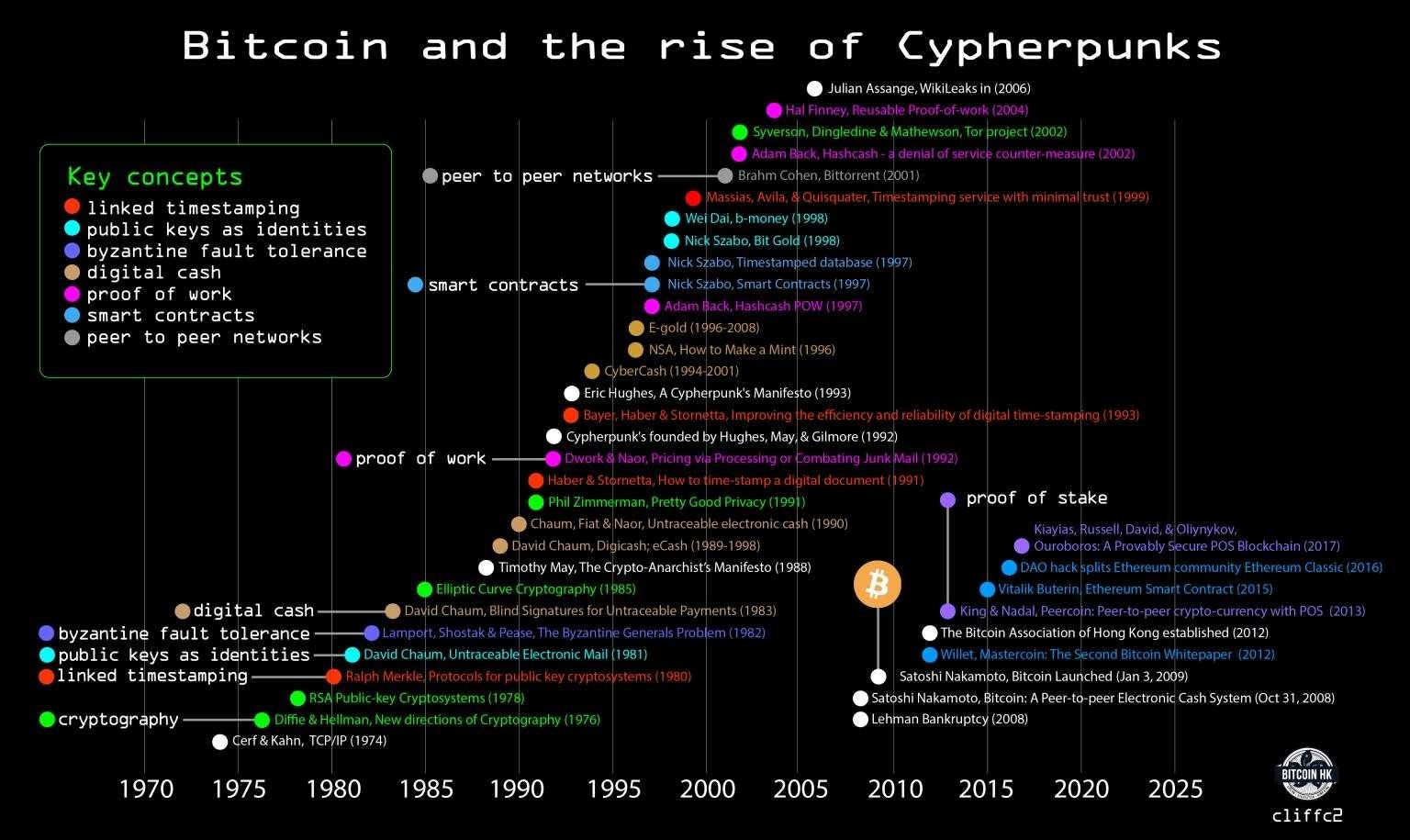
The idea of a private, state-independent currency originated from the early innings of the “Cypherpunk” movement. Cypherpunk refers to a group of people in the late 1980s and 1990s, who recognized the necessity to protect people's privacy online by using cryptography:
Privacy in an open society requires anonymous transaction systems. Until now, cash has been the primary such system. An anonymous transaction system is not a secret transaction system. An anonymous system empowers individuals to reveal their identity when desired and only when desired; this is the essence of privacy.
Long before Cambridge Analytica, long before the Great Firewall of China, long before the Snowden revelations, the cypherpunks saw it coming:
A regime of online censorship and surveillance that would eclipse the open Internet.
The technical roots of Cypherpunk ideas have been traced back to work by cryptographer David Chaum on topics such as anonymous digital cash and pseudonymous reputation systems, described in his paper "Security without Identification: Transaction Systems to Make Big Brother Obsolete" (1985).1 Over the next several years, these ideas morphed into the cypherpunk movement.
Much the work and writings of that movement would later become the foundation of Bitcoin:
Bitcoin
In late 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin white paper, titled a "peer-to-peer electronic cash system", to the "Cypherpunks" mailing list. He conceived Bitcoin as an alternative to the current financial system:
The root problem with conventional currency is all the trust that's required to make it work. The central bank must be trusted not to debase the currency, but the history of fiat currencies is full of breaches of that trust.
Rooted in cypherpunk history, Bitcoin community was formed around the principles of freedom, transparency, decentralization, and privacy – all of which the current financial system seemed unable to provide.
If you’re not familiar with Bitcoin’s roots, you’ll never going to grasp the full beauty of it.
Here comes Web3 ✨
The vision and power of Web3 is to give power back to the users to own and transact digital assets in a self-sovereign way.
uh... what?
Here's an example: Lens.xyz (aka. a Web3 Twitter)
Lens is a Polygon based social protocol on which everyone can create their own social interfaces. If you want to build a new Twitter, just build a new interface.
Since users connect with their wallets, they are able to take their profiles and all their data, stored as NFTs, with them.
It transfer full rights and complete ownership of content into the hands of users.
This is in contrast to today's digital world controlled by platform monopolies, such as Facebook, Twitter, or Google, that extract and monetize user data and privacy.
Kayvon Tehranian, Founder & CEO Foundation:
“The decentralized technologies powering this auction will fundamentally reshape our world — precisely to curb the abuse of power we spoke out against.”
We have a long road ahead, but the vision is here.
Let’s build it.
Onwards! 🚀
– Marc
Further reading:
Beyer, E. J. (2023, January 10). Edward Snowden teams with Pentagon Papers' whistleblower for NFT Auction. nft now. Retrieved January 11, 2023, from https://nftnow.com/news/edward-snowden-teams-with-pentagon-papers-whistleblower-for-nft-auction/
Dixon, C. (2018, October 26). Why decentralization matters. Medium. Retrieved January 11, 2023, from https://onezero.medium.com/why-decentralization-matters-5e3f79f7638e
Johnson, S. (2018, January 16). Beyond the bitcoin bubble. The New York Times. Retrieved January 11, 2023, from https://www.nytimes.com/2018/01/16/magazine/beyond-the-bitcoin-bubble.html
Shilina, S. (2022, October 7). What is Lens Protocol, and how does it work? Cointelegraph. Retrieved January 11, 2023, from https://cointelegraph.com/news/what-is-lens-protocol-and-how-does-it-work
Variant Team. (2022, October 19). The ownership economy 2022. Variant. Retrieved January 11, 2023, from https://variant.fund/articles/the-ownership-economy-2022/
David Chaum is a computer scientist and cryptographer known for his pioneering work in the field of digital privacy. He is the creator of the digital cash system ecash, the first anonymous digital payment system, and the development of the first digital mixers that enable anonymous communication over the internet. He is considered a pioneer in the field of digital privacy and is often referred to as the "father of digital cash." He also co-founded DigiCash, an electronic cash company, in 1989 and several other startups companies in the same field.